
Contents
In the realm of online advertising, there's a tricky strategy called ad cloaking and URL cloaking that's causing headaches for brands. What is this cloaking? It's a sneaky method used by dishonest webmasters to deceive search engines and users and hide their violations.
One well-known tactic is brand-bidding, where competitors and affiliate partners bid on branded keywords to get lots of cheap traffic and make money. The problem is, they're also hiding their violations, making it difficult for brands to catch them and take action.
To make matters worse, some webmasters use cloaking techniques to hide that they're targeting branded queries. This makes it even harder for brands to identify and address hidden ads effectively.
Here, we'll explore the definition and concepts of ad cloaking and URL cloaking, uncovering the methods used by dishonest webmasters and understanding the challenges faced by brands. By learning about cloaking examples and techniques, brands can protect their online reputation and ensure their search results truly represent their brand.
Learn more about affiliate link cloaking best practices .
How Cloaking Works
Once again, what is cloaking? It is a deceptive technique used by webmasters and operates in various forms. There are three types of cloaking: black hat, gray hat, and white hat.
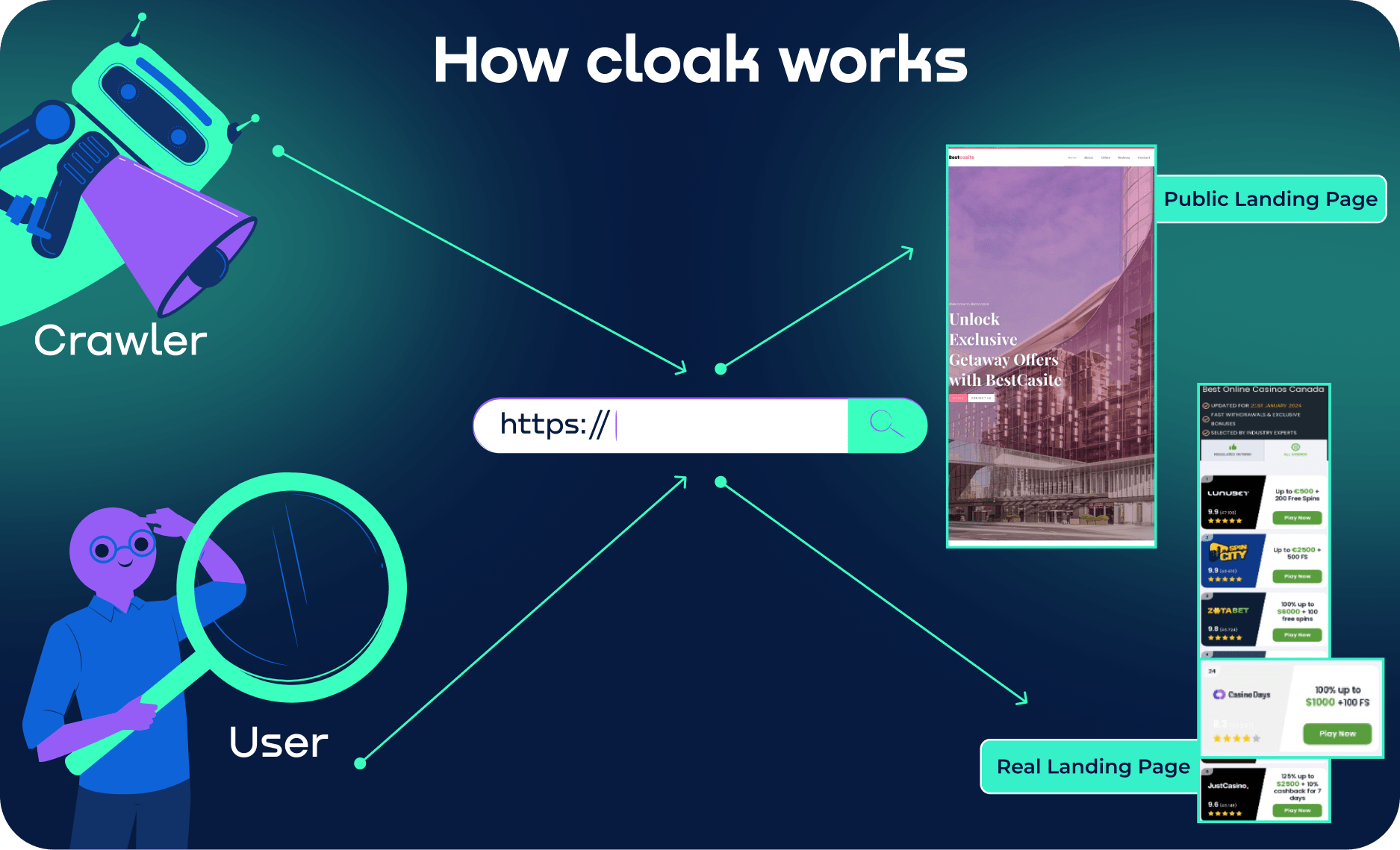
Black Hat Cloaking: This deceptive technique that involves presenting different pages to bots and ad reviewers, while directing human visitors to a different offer page. Unfortunately, this practice goes against search engine guidelines and aims to deceive search engine moderators by showing an acceptable page while leading users to a different, potentially harmful, page.
Gray Hat Cloaking: Gray hat cloaking falls into a gray area. It doesn't directly violate guidelines but still uses manipulative tactics. For instance, it displays different content based on users' locations. While not explicitly prohibited, gray hat cloaking leans towards questionable practices.
White Hat Cloaking: In contrast, white hat cloaking is transparent and follows search engine policies. It focuses on improving user experience without manipulation. This technique ensures relevant and accessible content for the intended audience.
Understanding the definition of cloaking and its types is important for brands to navigate online advertising. By being aware of these practices, brands can effectively combat hidden ads, protect their online reputation, and build trust with their audience.
Impact on Marketing Industries
Cloaking is a problem in various industries, including digital marketing, performance marketing, and affiliate marketing. Professionals such as digital marketers, PPC managers, SEO specialists, in-house affiliate managers, performance marketing agencies, and CPA networks need to be aware of this issue. They should actively detect and address ad and URL cloaking examples to ensure transparency and ethical practices in Google search. By doing so, they can deliver the best results to their target audiences.
Can Ad Cloaking be Considered Legitimate?
There is a debate regarding the legitimacy of ad cloaking. Some argue that it can be used for good reasons, like hidden ads based on user interests or location. It can also help filter out fake traffic such as spy bots and VPN servers.
However, it's important to note that ad cloaking goes against Google's standards. It involves deceiving users, publishers, and ad platforms. Depending on its usage, ad and URL cloaking can lead to a negative user experience or pose security risks. It may redirect users to non-compliant content or be used for malicious activities like mining or phishing.
How to Detect Ad Cloaking?
Publishers can identify ad and URL cloaking in Google by monitoring certain performance metrics:
CTR Spikes: Sudden increases in click-through rates may indicate an ad that appears normal but becomes clickbait when targeted.
Drop in CPMs and Viewability: If a hidden ad bypasses an ad platform's security, advertisers' traffic and spending may be diverted to fake sites, resulting in lower viewability and CPMs.
Negative Metric Changes: A sudden rise in bounce rate, reduced time spent on a site, and decreased traffic suggest a poor user experience, leading to negative metric changes.
Decline in Site Revenue: Poor-quality cloaking ads that provide a bad user experience can cause significant revenue loss if not addressed properly.
Marketers and publishers should be aware of the risks associated with ad and url cloaking and take necessary steps to ensure a positive user experience and compliance with industry standards. Brands had better use a cloaking checker to protect their online reputation by detecting and addressing deceptive tactics effectively.
The Importance of Monitoring Cloaking for Brand Bidding and Web Tactics
It's crucial to keep an eye on cloaking, especially when it comes to brand bidding. Cloaking is a sneaky trick used by webmasters to hide prohibited traffic, which can harm your brand.
To tackle this issue, it's important to stay alert and use cloaking checkers and brand bidding tools like Bluepear. Bluepear is a service that helps marketing teams, especially those focused on performance marketing and CPA advertising. They ensure ad integrity and prevent cloaking.
At Bluepear, we have advanced technical capabilities that allow us to uncloaked links and identify violators. Our selection of countries and quick proxy server rotation make it easy to access blocked websites. We automatically detect cloaking on designated sites, but we also offer a manual option for quicker results. Plus, we can capture screenshots and collect landing pages as proof of violations. With Bluepear, brands can safeguard their brand reputation and ensure fair competition.

Marketers can use brand protection tactics, maintain user trust, and effectively combat sneaky ad and URL cloaking tactics by partnering with Bluepear and implementing solid monitoring practices. Prioritizing transparency and ethical marketing practices is key for successful digital advertising strategies.
Learn about accurate affiliate tracking tools.

