
Contents
Redirect chains are a big problem for online businesses in 2025. Why? Because scammers are now using them to hide affiliate links and change traffic in a perfect way. HUMAN's research shows that attackers use the delays caused by these chains to make it look like users are engaging with ads and fool advertising tracking systems.
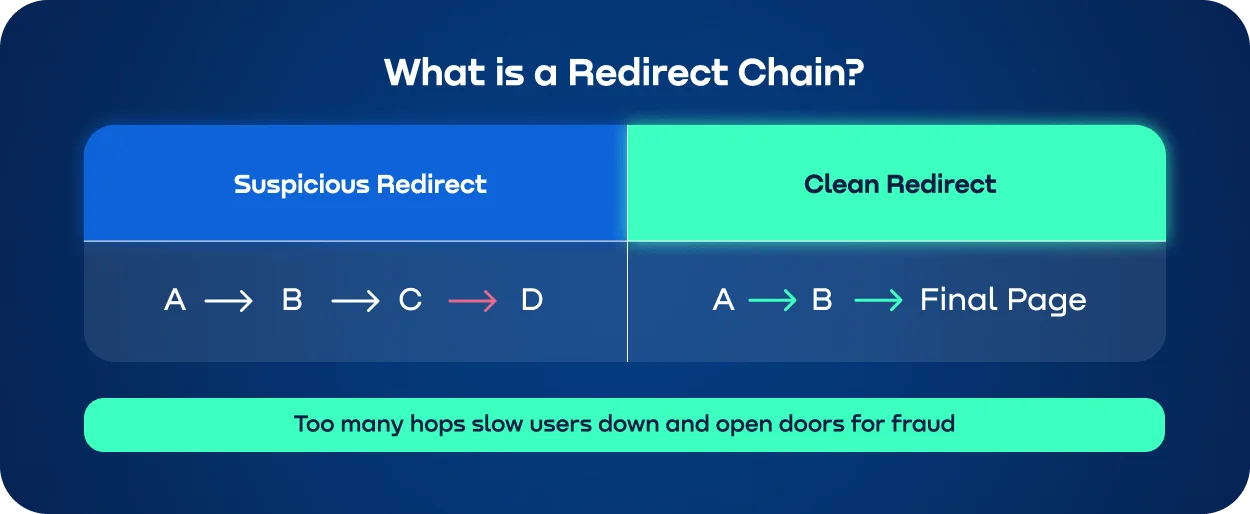
So, what is a chain of redirects? You click on link A, which takes you to B, which takes you to C and so on. It's that easy. The more redirects there’re, the longer it takes for the page to load. It makes the user experience worse and can lower search engine rankings. A full redirect chain checker can help you find these problems early on.
The problem isn't just with SEO, though. Scammers use redirect chains to secretly send users to pages with fake affiliate links. This means they illegally increase their commissions at the brand's expense. This practice, known as affiliate hijacking, is a serious threat to advertisers.
In this article, we'll examine how redirect chains hurt your SEO and PPC efforts, how scammers operate and how Bluepear detects and puts a stop to these schemes.
What is a redirect chain?
As we’ve already mentioned, a redirect chain is when page A automatically redirects the user to B, which in turn leads to C and so on. The longer the chain, the more time it takes to load the page, the slower the site runs, and the worse the user experience. A simple redirect checker like Bliepear can visualize this entire path and spot unnecessary hops.
Don’t confuse the chain with the redirect loop: there’s an end page in the chain where the user ends up. In a loop, the page redirects to itself endlessly and the user or the search robot never reaches the target.
There are two main reasons why redirect chains happen: mistakes or scams. When you move a website to HTTPS or change its structure, for instance, technical errors happen all the time.
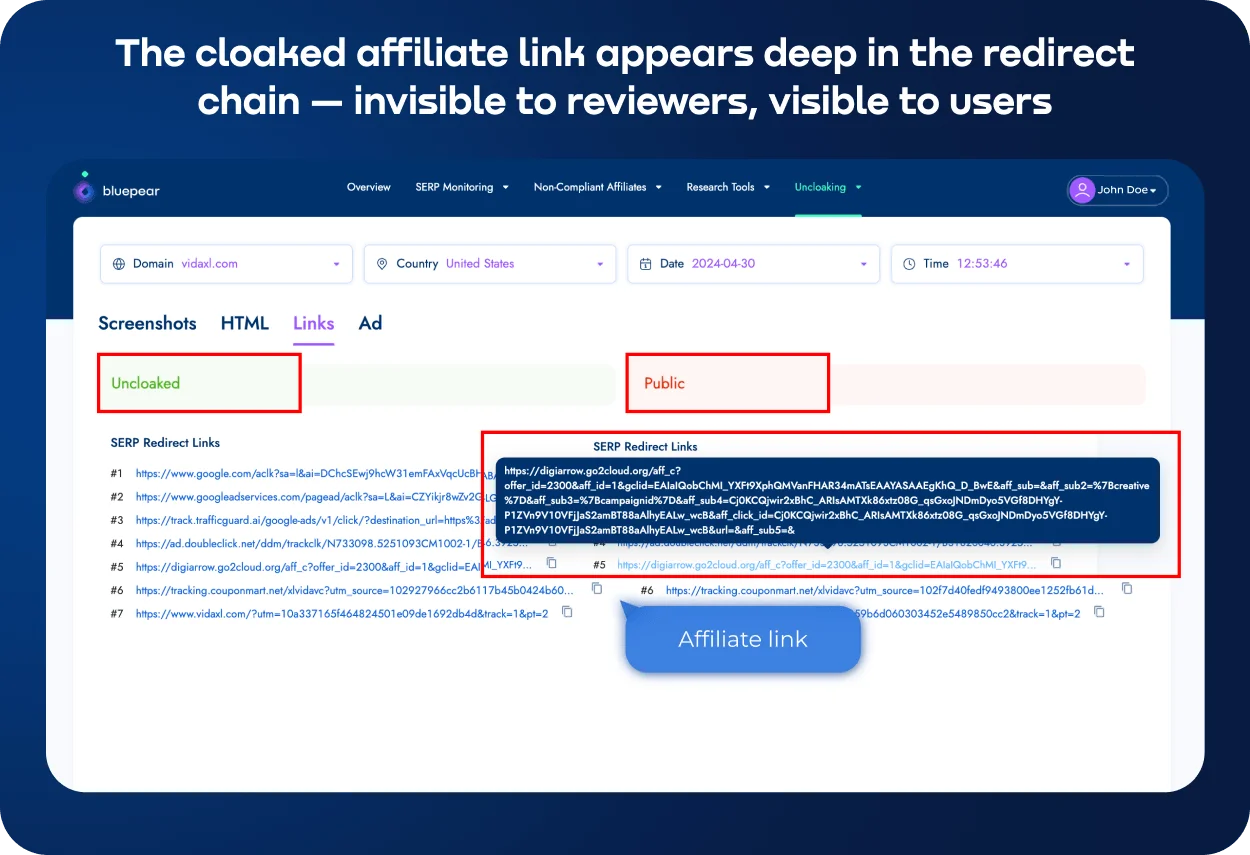
But fraud scammers use redirects to hide affiliate links and fraud scammers use redirects to cloak affiliate links and fake coupon pages, making cloaking detection a critical defense. They often use a proxy redirect to hide where the traffic is coming from even more.
Research published in 2025 (Not Here, Go There: Analyzing Redirection Patterns on the Web) found that roughly 50% of all tested URLs with redirects failed to reach their intended destination. The rest ended in errors or exceeded the allowed number of hops. Misconfigured redirects such as leaving temporary 302s where a permanent 301 is needed, can limit Google’s indexing and dilute link equity. And correcting such errors can take 3-6 months which becomes a significant loss for the business.
By understanding the redirect chains, you’ll be able to understand which errors on the site affect search positions and traffic and which schemes scammers can hide.
Why redirect chains are dangerous for SEO and PPC
Redirect chains may seem like a minor technical detail, until they start affecting your site’s visibility and advertising performance. From an SEO perspective, each additional referral consumes the crawl budget. Googlebot spends resources navigating through the chain and may not reach the landing page.
Search engines perceive too long chains as a soft 404 and each intermediate page weakens link equity, reducing the value of external and internal links. In addition, redirects slow down page loading, impairing the user experience and indirectly affecting search positions.
For PPC and affiliate campaigns, the problem looks even more serious. Scammers use redirect chains for ad hijacking: a user clicks on an ad, but ends up on a hidden page where the partner receives a commission. Bluepear as effective redirect detection flags suspicious chains so marketers can react quickly.
How do scammers keep from getting caught? They use cloaking by device or time to only send people to other sites on mobile devices or after hours. It hides what they're doing from the brand. Scammers also hide affiliate IDs, which makes it harder to keep track of and control payments. To fight these tactics, you need smart cloaking detection that can find these well-hidden plans.
The topic of redirect chains affects different roles within the company: SEO specialists monitor the indexing of pages, PPC marketers monitor the effectiveness of campaigns, affiliate managers monitor the correctness of payments and the IT team solves technical issues and corrects unnecessary redirects.
| Role in the company | Why it’s important |
|---|---|
| SEO Specialist | Manages crawl budget and link equity through redirect detection |
| PPC Marketer | Protects advertising budget from ad hijacking |
| Affiliate Manager | Tracks masked affiliate IDs and enforces program rules with a redirect checker |
| IT or Web Developer | Fixes unnecessary redirects and prevents loops |
How to find hidden schemes and redirect chains
Redirect chains can be surprisingly hard to find. Links that work fine on your computer may not work the same way on your phone or in another country. Some affiliates use geo-targeting to set up redirects that only work for users in certain areas or at certain times of the day. This is called dayparting.
This means that a quick, manual check might not catch hidden manipulations, and even experienced teams might not see the problem without the right tools, like a Bluepear redirect chain checker.
Bluepear's uncloaking system solves this problem by mimicking how real users act on different devices and in different places. Full URL paths and HTTP status codes are recorded for each redirect in a chain. This provides powerful redirect detection.
The system also takes screenshots of the last page and the search results, which makes it easy to see where the traffic really goes. This level of detail helps teams not only figure out if a redirect exists, but also how it works in different situations and for different groups of people.
There’re separate dashboards for Affiliates and Competitors that show the results. Each case is marked as New, In Progress, or Resolved. This labeling helps teams figure out which investigations are most important.
For example, a new redirect chain that leads to a hidden affiliate page can be fixed right away, but older problems are kept an eye on until they are completely fixed. You can export screenshots and URL logs for more in-depth analysis, internal reporting, or keeping track of commissions that were sent to the wrong person.
Here’re some real-life examples of how these hidden chains work: an affiliate might send traffic through several intermediary pages that look real at first glance, but they actually send users to a page where their actions help the affiliate at the brand's expense. Chains like these can vary depending on time of day or location which makes redirect detection even trickier without automated scanning.
Teams can see exactly how traffic flows, which links are acting suspiciously, and which affiliates or competitors are involved by combining testing at multiple locations and on multiple devices with detailed logging and visual evidence. It helps find hidden plans early, before they affect how users experience the site, how well ads work, or how accurate reports are.

How to fix and stop redirect chains
The next step is to deal with redirect chains. By making sure that users and search engines go straight to the right page, streamlining redirects cuts down on unnecessary detours. It fixes SEO redirect paths that don't work.
Redirect rules can be hard to follow, especially when you use temporary 302 redirects instead of permanent 301s or when HTTP to HTTPS and www to non-www rules overlap. These little mistakes can make long chains without anyone noticing, which hurts SEO and makes analytics less accurate. Auditing and fixing them with a redirect checker helps keep track of things correctly and keeps link equity. Many companies schedule a Bluepear to catch new chains before they grow.
Affiliate programs are getting harder. Some partners send traffic through several pages to make more money. It's hard to find these redirects by hand because they may only happen at certain times or in certain places. Clear rules that say no hidden redirects, cloaked links, brand PPC, or fake coupon pages set limits and lower the chance of abuse, which is supported by constant cloaking detection.
New chains can show up when sites change or affiliates change their links. Teams can find and fix problems quickly by regularly checking URL logs, HTTP statuses and screenshots that have been taken.
Getting rid of unnecessary redirects and making the rules for affiliates clearer had an immediate effect. Pages started to load faster, users got to the content they wanted without having to go through extra steps. Then traffic data started to show real behavior instead of being skewed by hidden chains.
At the same time, it became easier to keep track of affiliate activity. Any attempt to send users through extra pages was easy to see, so the team could act quickly before it hurt campaigns. Over time, this approach reduced the risk of revenue loss and preserved the value of inbound links, turning what was once a hidden problem into a manageable part of site and affiliate management. Hidden schemes and how to detect them
Some affiliates or competitors hide their activity through extra redirects or disguised links. The table below summarizes the most common schemes, their impact, how to detect them and what evidence to keep.
| Scheme | What is affected | How to detect | What to keep |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliate Cloaking | Affiliate commission tracking, campaign ROI | Compare landing page URL and final URL, monitor geo- and device-specific redirects, use cloaking detection tools | Full redirect path, screenshots, timestamps |
| Ad Hijacking via Redirect Chains | PPC budget, ad performance | Track unexpected intermediate pages with a redirect chain checker, check for unusual traffic spikes from paid ads | List of URLs, HTTP statuses, screenshots |
| Fake Coupon or Bridge Pages | Conversion data, user experience | Scan coupon and deal sites, test affiliate links on multiple devices and locations | Screenshots, affiliate IDs, full chain URLs |
| Geo or time based redirects | Analytics, SEO indexing | Run multi-geo and multi-time tests with a redirect checker, compare results to expected landing pages | Complete logs of URLs, timestamps, device or geo info |
Conclusion
Redirect chains is a way for scammers to hide traffic and steal commissions. It slows down the download, consumes the crawl budget and reduces the position in the search, and for brands with partner programs means direct financial losses.
Constant monitoring with a reliable redirect chain checker and strict rules for partners are the only reliable way to protect the site and advertising budgets. Bluepear captures redirect chains in different geos and on different devices, saves evidence and notifies the team in real time so that violators can be quickly blocked and commissions refunded.
Start monitoring today: connect Bluepear to see all the redirect circuits and hidden circuits within the first day.
FAQ
1. Why should I care about redirect chains?
They slow down website loading, waste the crawl budget of search engines and reduce their position in search results. For brands with affiliate programs, this’s also the risk of losing commissions due to fraudsters. Using a redirect checker is the first step to protection.
2. How does the redirect chain differ from the loop?
There’s an end address in the chain: A to B to C. In the loop, the redirection is looped: A to B to A, and the user cannot get to the landing page.
3. How can I tell if a partner is masking an affiliate-ID?
Signs: different URLs when clicked and in the browser bar, sudden spikes in traffic from certain regions or at certain times of the day, inconsistencies in conversions. Advanced redirect detection tools automate this process.
4. What tools help to find redirect chains and hijacking?
In addition to the standard SEO checks described in the material, automatic multi-geo and multi-device monitoring plays a key role. Bluepear as a redirect chain checker scans pages from different countries and on different devices, captures complete URL chains and preserves evidence of violations.
5. What should I do if I find a redirect chain?
Delete the extra 301/302, redirect traffic directly to the final URL, check the affiliate links and record evidence for a possible clawback. A good redirect checker will help identify all steps in the chain.
6. Isn't one 301 redirect harmful?
A single 301 is safe. The problems begin with several consecutive redirects: the search engine may not reach the final page and the link weight is lost.
7. How does Bluepear help automate the process?
The platform performs multi-geo and multi-device scans, saves screenshots and full URL chains with HTTP codes, sends instant notifications to Slack or email and generates reports to block violators and refund commissions, serving as an all in one redirect chain checker and cloaking detection system.

